Should you practice boat pose or navasana with an extended spine, or is it okay to let your back round a little bit?
Yoga teachers commonly teach navasana with cues like “Straighten your spine,” or “Lift your chest and pull your shoulders back,” but is that always the best way to practice it?
You may think of navasana as an abdominal exercise, but the primary muscles at work in the pose are the hip flexors, the muscles that bring the front of the pelvis and the thighs closer toward each other, creating a fold at the hips. Your abdominal muscles play a supporting role, but they don’t attach to your thighs, so they can’t pull your legs and trunk toward each other. That’s the job of the hip flexors.
The hip flexors
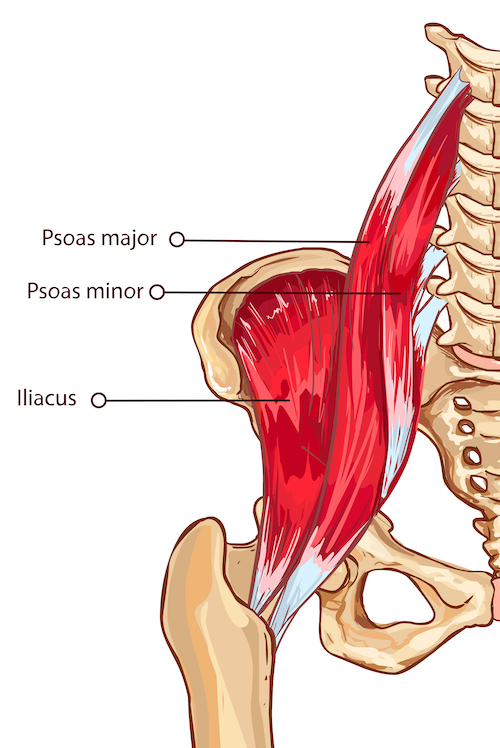
The major hip flexor muscle group is the iliopsoas, which consists of two main muscles. One, the iliacus runs from the inside of the ilium, the upper rim of the pelvis, to the lesser trochanter on the inner upper thigh bone, or femur. When it contracts it pulls the thigh toward the front of the pelvis—or, if the thigh is fixed, the pelvis toward the thigh.
The other major muscle of the iliopsoas is the psoas major (there is also a smaller muscle, which not everyone has, called the psoas minor). The psoas major originates on the front of the lumbar spine and joins with the tendon of the iliacus to insert onto the lesser trochanter. When it contracts, it pulls the the lumbar spine and the femur toward each other, flexing the hip.
There’s also another important hip flexor working in navasana. The rectus femoris is one of the quadriceps muscles, the large muscles on the front of your thigh that straighten your knee. It originates on the pelvis at the anterior inferior iliac spine, just above the hip joint, and runs along the front of the thigh to insert onto the patella, or kneecap, through the common quadriceps tendon, which then attaches through the patellar ligament to the front of the tibia, or shin bone. Like the other three quadriceps muscles, it acts to straighten the knee. But unlike the others, it attaches to the pelvis, making it a strong hip flexor as well.
What’s happening in navasana?
In navasana, the iliopsoas contracts to pull the lumbar spine toward the thighs, which tends to arch the lower back. Some degree of spinal extension is probably necessary to stay lifted; if the lower back rounds too much, you’ll roll backward. At the same time, the abdominal muscles work to stabilize the lumbar spine. The rectus femoris works as well, both to flex your hips and, if you’re practicing with straight legs, to extend your knees.
Students sometimes feel the rectus femoris gripping, or even cramping, at the front of the thigh in navasana. You can reduce that by bending your knees. That’s partly because bending your knees shortens the lever arm of the legs, making your legs effectively lighter.
But there’s another reason why bending your knees may make the pose feel easier, which has to do with the fact that the rectus femoris is a two joint muscle, crossing both the hip and the knee joint.
Many two joint muscles are unable to create a full range of motion across both joints at the same time—a phenomenon called active insufficiency. That’s because muscles work by contracting or shortening. Once a muscle is already shortened, it can’t contract much more, making it ineffective at creating further movement.
If you practice navasana with your legs straight, the poor rectus femoris is working simultaneously to straighten the knees and to flex the hips. No wonder it may feel like it’s cramping.
Not only that, the psoas major is also a multi-joint muscle. It crosses multiple joints in the lumbar spine, as well as the hip joints, so it’s also likely to run into active insufficiency.
How can you make navasana easier?
If you struggle with navasana, you may find a more ease in the pose by lengthening those over-shortened muscles so that they can work more effectively.
How would you do that? One way would be to bend your knees, which will lengthen the rectus femoris across the knee joint. Or, if you practice navasana with straight legs, you could do the same thing by rolling the pelvis backward a little, lengthening the rectus femoris across the hip joint.
Over-arching your lower back in navasana also disadvantages the psoas major for the same reason. Rolling your pelvis backward a little will pull your lumbar spine backward, lengthening the psoas major and making it more effective as a hip flexor.
So, if you find yourself straining in navasana, it may help to explore how much your spine actually needs to extend to keep from falling backward. If you allow your back to round a little bit, will that help you find a bit more ease in the pose?
As with any asana, there’s no one right way to practice navasana. For some people, rounding the back may be problematic (for instance, if they have a herniated lumbar disk). For others, arching the back creates strain. But if you’re open to exploring within the pose rather than simply following what is supposed to be the “right” alignment, you’ll find the way that works best for you.